People analytics is an HR discipline that involves collecting and analyzing employee-related data to gain insights into various aspects of a workforce and make data-driven decisions. They’re used to improve hiring, employee experience, engagement, retention, and business outcomes.
Increasingly, HR professionals are using rapid data gathering techniques and data analytics platforms to acquire and demonstrate where there are direct correlations between their actions and the overall business performance.
See how Qualtrics People Analytics can help accelerate business success
What is people analytics?
Also known as workforce analytics or HR analytics, people analytics is a data-driven and outcome-focused approach (or method) of analyzing all people-related processes, functions, challenges and opportunities at work. Simply: it’s about analyzing people data to solve business problems.
With people analytics, organizations can make smarter, more strategic, and data-backed talent decisions throughout the employee lifecycle – from more diverse hiring decisions and better performance management to improved retention rates.
People analytics inform data-driven insights to improve the way your organization does business – and the impact HR has on the bottom line.
Human resource programs no longer need to be based on “soft” reasoning but should be as analytical and as data-driven as any other management discipline.
– Chris Argyris, Management Theorist & Professor Emeritus, Harvard Business School
What types of people analytics should I measure?
To use people analytics to support your organization, you need to look at four different types of data across the organization:
1. Organizational performance metrics
At the top level are the organizational performance metrics that employee actions influence.
Data analytics platforms help the HR department identify where there are direct correlations between their actions and overall business performance.
The key organizational performance metrics that people analytics impact are:
- Revenue per employee – revenue divided by the number of employees in the organization.
- Operating margin – profit represented by the percentage of revenue left over after all operating expenses are subtracted.
- Earnings per share and total shareholder return – a measurement of the amount of profit or value a holder of one share of the company would receive.
- Return on assets (ROA) – net income divided by assets.
2. Workplace monitoring metrics
These are the basis of a “big data” set when they are merged with the other data sets to pinpoint which individual and combined elements influence the key organizational metrics. These include:
- Open hiring requisitions
- Time to fill open requisitions
- Cost per hire – including costs from recruiters, job advertising, talent management systems and the cost of senior leaders interviewing candidates
- Number of candidates/interviews per hire
- Worker productivity
- Worker quality
- Absentee rate
- Safety incidents
- Voluntary vs. involuntary terminations
- Average performance rating
3. Key customer metrics
These are typically gathered and tracked by marketing or customer experience (CX) teams. A centralized, combined database of HR and CX data is integral to analyzing and tracking the impact your team has on the metrics that define the outcomes of your HR work.
Because employee experience affects customer experience, customer-based metrics are strongly connected to your employees’ actions.
Both the key customer metrics and workplace monitoring metrics above are strongly influenced by voice of the employee data. When you are running a combined data analysis it’s important to explore how changes in voice of the employee data influence key customer metrics, workplace monitoring metrics and organizational performance metrics.
Typically, marketing or customer experience teams gather and track this information, and by collaborating with those teams you can create a centralized and combined database of HR processes and customer data. When you analyze and track the impact your team has on these metrics, you’ll be able to further define and refine your outcomes and deliver the most business benefit.
Some of the most common customer metrics are:
- Customer satisfaction
- Net Promoter Score
- Share of wallet
- Number of products purchased
- Customer retention
- Average revenue per customer
- Profitability
4. Voice of the employee data
This helps organizations understand employee behaviors, opinions, concerns, ideas, grievances, suggestions and perspectives and other qualitative data. It uncovers the factors with the largest impacts on organizational performance, workplace monitoring, and key customer metrics to help draw new conclusions and pinpoint actions, management techniques, and operational changes.
These metrics are usually gathered using:
- Pulse surveys
- 360-degree feedback
- Lifecycle monitoring
- Performance reviews
- One-on-one meetings
- Onboarding
- Exit interviews
- Candidate experience surveys
- Development program evaluations
- Assessment results
Increasingly, employee journey analytics and employee listening solutions are augmenting the traditional employee surveys.
Each of these data elements will inform and influence different areas of the organization, but when analyzed together, will provide a compelling business case for how and why you want to execute any sort of initiative, project, or program.
Identify which metrics you hope to influence at each level and how you hope to influence them by showing the correlations (or connections) between each effort and metric.
What are the benefits of people analytics?
We’ve explored the types of HR data to gather and measure as part of a people analytics program.
Here are the benefits of doing so:
- Make data-driven decisions: People analytics takes out the guesswork and helps you make evidence-based decisions about your workforce. Using employee data analysis, you can surface insights into areas such as talent acquisition, performance management, employee engagement, and retention. When your decision-making is data-driven, you minimize bias, become more objective, and make informed choices that are more likely to deliver positive business outcomes.
- Enhance business performance. Businesses that use people analytics to make better decisions enjoy 82% higher three-year average profit than their low-maturity counterparts. By analyzing employee productivity, absenteeism, turnover, and salary data, you’ll be able to pinpoint opportunities to cost-save, be more efficient, and allocate resources effectively.
- Improve diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI). Identifying metrics for diversity ratios at every stage of the hiring process helps ensure equity throughout it. By analyzing diversity metrics, pay equity data, and employee engagement surveys, you’ll be able to identify gaps, design interventions and track progress to create a more diverse, inclusive, and equitable work environment.
- Tackle your turnover problem. People analytics allow you to identify the cost savings of retention programs by analyzing the direct and indirect costs of turnover relating to compensation, absenteeism, productivity, and learning and development.
- Build a world-class employee experience. Every interaction an employee has with an organization is a data point that can be utilized to glean insights – and improve EX.
- Forecast workforce needs: People analytics can predict future talent requirements, succession planning, and required skills by analyzing patterns in employee performance and turnover. They can identify high-potential employees, track individual and team performances, and inform talent development initiatives to futureproof your business.
- Solicit investment in your programs. Show the C-suite the impact of your initiatives over time and convince them to keep investing in your work by predicting the outcomes of your efforts.

Many companies strive to make their sales force more effective and efficient, but few look at them through the lens of people data to do so. At Johnson & Johnson, we ask ourselves: what characteristics do successful salespeople have in common? How can we recruit and develop our people to replicate traits that will lead to success? People analytics can help answer these questions in a way that drives direct business impact.”
– Piyush Matur, Global Head of Workforce Analytics at Johnson & Johnson
What does a people analytics program look like?
Like many organizations, Ford Motor Company relied on broad, traditional surveys to understand how employees were feeling.
“After extensive research, we realized the organization would benefit from more focused, frequent, and comprehensive employee sentiment data,” said Dr. Marina Pearce, Global Talent Analytics Lead at Ford.
As a result, Ford developed an ‘ask-listen-observe’ approach — this involves compiling active and passive data elements to tell a more comprehensive story (versus the data collected from just one survey per year, as an example).
| What Ford does | Where (and how) Ford collects data | |
|---|---|---|
| Ask | In a very structured way, Ford explicitly asks people to give their opinions and feedback on a particular thing. | Focus groups Pulses Surveys Polls Interviews |
| Listen | Ford listens to employees, which is a very unstructured way to learn what your employees are naturally talking about in a public forum | Social media posts Glassdoor reviews Informal discussions during meetings |
| Observe | Observing is about quantifying behavior around a specific sentiment topic (such as culture change). | Ex. culture change — if Ford wants to know the employee behaviors around culture, they measure Are employees attending events about culture? Are they watching videos about culture? Are they downloading culture playbooks? |
Combining those ‘ask-listen-observe’ results, Dr. Pearce and her global talent analytics team then share them with Ford’s internal decision-makers to help shape new programs to meet the needs and desires of employees.
What does a people analytics team look like?
The composition of a people analytics team will vary depending on your business’s size, industry, and specific requirements. Some teams have people who cover multiple roles, while larger organizations may need more specialists. What is important, though, is that HR professionals, the IT department, and business leaders collaborate and communicate to make sure that people analytics insights get disseminated and actioned throughout the whole organization.
A people analytics team may consist of:
- A people analytics manager or lead: to oversee operations, liaise with other departments, set strategic goals, manage projects, and ensure they meet organizational objectives.
- Data analysts: To collect, clean up, and analyze workforce data. They use statistics to identify correlations, trends, and patterns, and communicate their findings through reports and presentations.
- Data scientists: Skilled in statistical modeling, machine learning, and predictive analytics, they use algorithms to surface insights and build predictive models to help workforce planning, talent acquisition, and retention.
- HR specialists: Subject matter experts who can help interpret data in a human resources context. They collaborate with the people analytics team to translate HR issues into analytically solvable problems, communicate business needs, and outline what data is required.
- IT Specialists: Responsible for data infrastructure, data integration, and data governance. They are also responsible for data security, accuracy and accessibility, collaborating with other IT teams to manage company-wide data systems and tools.
- Visualization designers: They help transform complex data analysis into formats and stories such as dashboards and visual reports that are easy to understand.
How do I get started with people analytics?
Here’s how to get started with people analytics to make data-driven decisions and improve employee experience at your organization:
1. Assess the readiness of your organization
Are members of your board or C-suite asking about ways to improve efficiency? Have business leaders (in other departments) discussed the positive ROI of analytics and technology? If the answers to these questions are yes, your people analytics program is already in good company.
2. Identify your data champions
Finding fellow (internal) data champions can help you get buy-in, build your business case, and navigate any potential cultural changes as a result of putting people analytics to use.
3. Formulate impactful questions
To draw insight into your organization, look at your overall business goals. Determine how HR and EX fit into those goals, then work backwards to the types of questions you’d like answered – and the areas you want to improve on.
4. Be prepared to look deeper into your data
People analytics will enable you to go beyond typical HR questions to understand the “why” – such as:
- Why are you overspending on your overtime budget?
- Why aren’t total rewards aligned with the actual needs and wants of your employees?
- Why are voluntary terminations increasing?
5. Choose your people analytics software
There’s a selection of cutting-edge tools available for employee listening, combining CX and EX, and analyzing the employee journey.
See how Qualtrics People Analytics can help accelerate business success
Trends in the field of people analytics to keep on your radar
In the post-pandemic world, where the future of work itself is uncertain, with high employee turnover rates, an exhausted workforce, evolving return-to-office policies, inflation, a shortage of workers and a looming economic downturn, there’s never been a greater need to take a data-driven approach to decision-making.
So, at this fragile time, underestimate people analytics solutions at your peril. The market size is currently estimated to be worth $1.7 billion (and growing quickly). So where are the challenges and the opportunities, and what do you need to keep on your radar?
1. AI-powered people analytics
Analytics tools powered by artificial intelligence (AI) have permeated every facet of HR, from recruitment to employee experience, right through to learning and development, and, of course, people analytics. Natural Language Understanding (NLU) machine learning and modeling do the heavy data lifting, freeing up business leaders to focus on the strategy and big-picture problem-solving.
AI lets HR professionals comb through vast amounts of data rapidly and accurately, identifying patterns and insights that might not have been immediately apparent. It helps the HR team make more informed decisions, for example identifying the best job candidates.
Predictive analytics help HR identify patterns and trends in the data that predict future outcomes, such as the employees who could be at risk of leaving, or the candidates who are most likely to make a real success of their role.
Employee sentiment analysis tools help business leaders listen to what employees and customers are saying, wherever they’re saying it.
Although the emergence of AI in these areas is making some roles redundant, it’s also creating new roles. According to one speaker, for every job that’s currently eliminated, 2-3+ jobs are created to support the building of AI infrastructure.
However, the main thing to watch out for is the potential skills gap within this area, as the expertise that’s needed for these new roles is different and often more advanced. The need for upskilling may become more urgent with time, so it’s crucial to get ahead of the curve.
2. More data-driven decision-making
It’s no longer enough to act ‘on a hunch’ or ‘take a punt’ on a business decision. Cutting-edge business demands the input of high-quality data to help make the decisions that drive better performance. Hugely successful companies go further and cultivate a data culture, knowing that data on its own is useless without analytics.
Data science consultants MillanChicago recommend focusing on the following four areas to help build a data-driven culture:
- Human resource processes: the right ones in place to run people analytics across the whole employee journey, from applicant tracking systems to exit surveys
- Human resource capabilities: data science specialists to run your people analytics project, who know best practices for data gathering, analysis and reporting
- Technology processes: the software, appropriate security and privacy policies to store and analyze data safely
- Technology capabilities: commercial platforms or bespoke solutions that can store, process and manage your gathered data
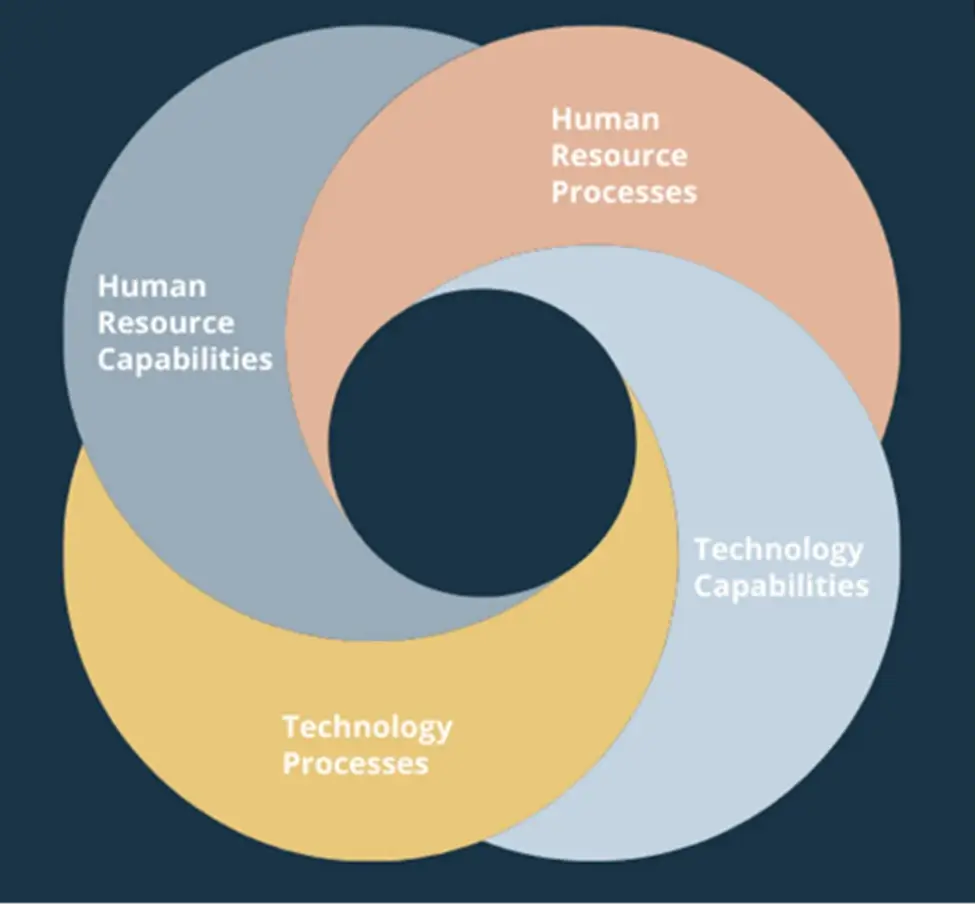
Image Source: millanchicago.com
3. Employee experience (EX) must be a priority
Employees make a much bigger commitment to their employer than consumers commit to a company and brand, so it will be essential to invest as much in the employee experience.
AI offers a great opportunity for improving EX when done right. For example, AI-powered chatbots, libraries and knowledge bases are perfectly placed to provide answers to HR-related topics and questions frequently asked by employees — allowing them to self-serve and get the information they need faster.
Employee sentiment analysis tools lets business leaders listen to what employees are saying, wherever they’re saying it.
You can analyze messages, calls, chat, and emails to your internal HR and technology service desk and uncover opportunities to improve the service experience. Then, you’ll be able to identify what is affecting employee experience across your whole company to take action and close gaps.
With Natural Language Understanding (NLU) applied to open-text feedback in employee engagement survey responses, you’ll be able to build up a detailed understanding of how every employee feels. From this, you’ll be able to identify hidden topics and understand:
- Why people are leaving, e.g. promotion, raise
- Where they are going, e.g. to competitors or a different career
- How this attrition is going to affect the company
A modern people analytics solution will be able to pinpoint what is going wrong with your employee experience so that you can fix it before you lose more good people.
4. More focus on Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI) and Belonging
A combination of 2020’s Black Lives Matter protests, and the irrefutable data that diverse companies are 1.32 times more productive than those that lack diversity has led to more focus on DEI. A data-driven culture can use people analytics to highlight incidents of unconscious bias, undiscovered workplace inequalities, and gaps in DEI training.
Leading organizations also know that a culture of belonging, which is the top employee experience driver linked to engagement and well-being, can be nurtured by listening to everyone in the workforce. The real-world data that results from people analytics can help make a great workplace even greater – and deliver stellar business results.
5. Storytelling with people analytics
Want leaders to pay attention to your analyses? Help decision-makers understand the meaning behind the numbers by humanizing and telling stories with data. One caveat though: these must always link back to a business challenge or they risk being overlooked.
Create strong narratives
The way to do this is by developing confident, coherent narratives. Direct these at those you’re trying to influence. But a word of warning: don’t get bogged down with the tools and methodology.
Humanize data
In the past, the goal was to democratize data and insights. Now the goal should be to humanize the data. This can be achieved through storytelling and making people aware of the impact this work can have for good. It’s not just fundamental; people analytics teams have a responsibility to do it.
Be realistic
There is a need to strike a healthy balance between ambition and reality — and some even say there’s no such thing as “big data” in HR due to limits in data sets.
For example, predictors or high-performance employees, manager bias, etc. aren’t yet as reliable as we need them to be. As AI and big data continue to evolve, HR leaders need to strike a balance between relying on these data sets and making human decisions to drive their workforce forward.
6. Empowering managers and activating the frontline
A few years ago, Harvard Business Review carried out a study with ThoughtSpot on the link between empowering frontline employees and organizational performance.
They spoke to nearly 500 business executives from 16 industry sectors in North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific.
And what they found was this: while organizations are more successful when they empower frontline employees, just one-fifth (20%) have a truly equipped and tech-enabled workforce.
Almost 9 in 10 (86%) agreed that their frontline workers need better technology and insight to make better decisions in the moment.
Of course, acquiring the appropriate technology is just the start — what’s crucial is that organizations activate their frontline workforce effectively… and that starts with empowering managers.
Managers are vital to every employee’s experience — and the success of the frontline. After all, they’re the ones distilling the strategies and objectives developed by leaders. However, 58% of managers claim to have received no training whatsoever.
The problem is that many don’t know where to start or how to take appropriate action — but as organizations invest in people analytics tools, they can empower their managers to uncover what the workforce needs, including opportunities for success and growth, and where the blockers are.
7. Linking people data to CX (and other business) outcomes
Every leader knows intuitively that by investing in their people, they can drive better business outcomes, and people analytics helps light the way.
The thing is: Employee Experience (EX) and Customer Experience (CX) are intricately linked — organizations that prioritize and enhance EX often see positive impacts on CX and overall business outcomes. For example, a renewed emphasis on employee development could lead to employees acquiring new skills that help their job function, and in turn deliver better business results.
Here are some ways in which EX drivers can influence CX and other business results:
Employee engagement and productivity
Engaged, satisfied employees are more likely to deliver exceptional customer service. When employees have a positive experience at work, they tend to be more motivated, committed, and productive. This, in turn, results in improved customer interactions, increased customer satisfaction, and loyalty.
Customer service excellence
EX can directly impact the quality of service provided to customers. When employees feel valued, supported, and empowered, they are more likely to go above and beyond to meet customer needs. Positive EX drivers, such as training and development, clear communication, and a supportive work environment, augment employees’ skills, knowledge and confidence, leading to better customer interactions.
Employee advocacy and brand ambassadors
Employees who’ve had a positive experience of their organization often become advocates for the brand. They are more likely to say positive things about their employer, inside and outside the workplace. Brand ambassadors like these can have a ripple effect on CX, as customers are then more likely to trust and engage with a brand that has such enthusiastic and satisfied employees.
Innovation and continuous improvement
A positive EX can foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within an organization. When employees feel empowered to share their ideas, provide feedback, and participate in decision-making processes, they contribute actively to CX enhancements.
Employee retention and talent acquisition
Organizations that prioritize EX, offering a positive work environment, growth and development opportunities, good work-life balance, and competitive pay and benefits often enjoy higher employee retention and attract top talent to come and work for them. This builds a stable, skilled workforce that consistently delivers excellent customer experiences.
Financial performance
There’s a strong link between positive EX, customer experience, customer loyalty, and financial performance. Satisfied and loyal customers are more likely to repeat purchase, and recommend to others, thereby contributing to revenue growth. And organizations with great employee experience tend to have lower turnover costs, higher productivity, and reduced recruitment and training, leading to better financial outcomes.
The ethics of people analytics
As people analytics involves collecting and analyzing personal and sensitive information, it’s essential that organizations respect this data, handle it with care, protect it from theft or misuse, and respect people’s privacy. In short, treat it ethically.
Here are the key ethical considerations around people analytics:
Data privacy and security
Employee data must be collected, stored, and used in compliance with data protection laws and regulations. You need to set up safeguards to protect this sensitive personal information and guard against unauthorized access or data misuse.
Informed consent
You need to communicate transparently when you ask employees to consent to their data being used. To get employees to trust your people analytics process, you need to tell them:
- What data is being collected
- Why it’s being collected
- How it will be used
- The implications for their careers and well-being
Freedom from bias and discrimination
You must make sure that people analytics data is analyzed and used in a fair and unbiased manner, avoiding discrimination based on protected characteristics such as age, gender, or race.
Data accuracy and integrity
You must make regular checks and validations to ensure the accuracy, quality, and integrity of your people analytics data.
Employee empowerment
You must give employees the opportunity to access their own data that they have given informed consent for.
Ethical governance and accountability
Organizations need clear policies, guidelines, and processes in place to ensure that people analytics data is used ethically. Provide protocols for employees to raise or clarify concerns around personal data. Designate specific individuals to be responsible for ethical standards compliance and
Continual evaluation and review
Society and regulatory requirements continually evolve, so you’ll need to regularly monitor and review your ethical framework and guidelines governing your people analytics data.
Redefine the experiences you deliver, today
Take a look at how our people analytics software can help you surface insights and take action on employee feedback. Armed with that information, you can present an incredibly compelling, data science-driven business case for how and why you want to execute any sort of initiative, project or program. You’ll be able to convince your CHRO to do anything.
See how Qualtrics People Analytics can help accelerate business success