Employee retention and growth are the most common reasons for implementing incentive compensation plans, but they can also be used to increase sales, employee recruitment, customer loyalty, commitment, and to fulfill business objectives. Are your incentive programs assisting you in attracting top financial services players and motivating your workforce to meet your company’s objectives? Long-term success depends on having the right strategy at the right time. Incentive plans are an essential part of holistic incentive compensation for the financial services industry.
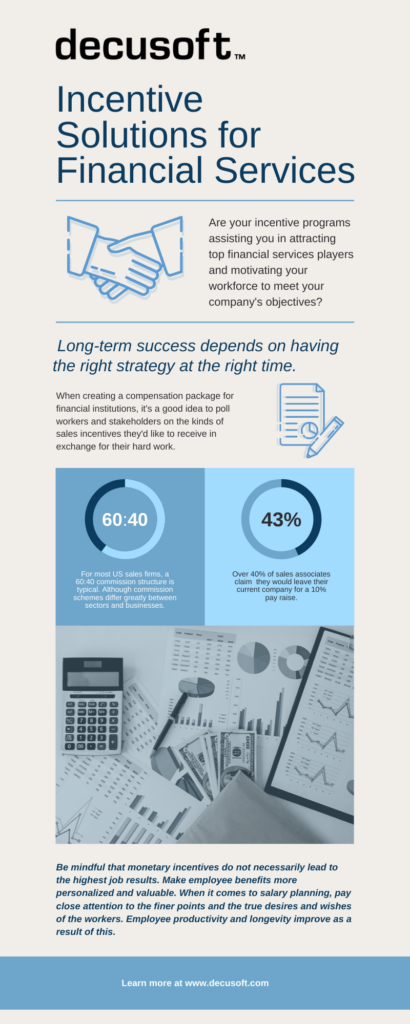
When creating a compensation package for financial institutions, it’s a good idea to poll workers and stakeholders on the kinds of sales incentives they’d like to receive in exchange for their hard work. Your human resources department, board of directors, and compensation committee should clarify how the payouts can empower employees and what level of achievement is needed to earn the reward. Make the methodology and eligibility requirements transparent to staff, as well as concrete targets and descriptions of success standards that workers must achieve in order to qualify for the benefit. Check back with the team on a regular basis to see how happy they are with the reward package and whether it is having a positive effect on employee motivation. Conduct departure interviews for employees who are voluntarily leaving the company to determine whether the retention pay plan influenced their decision to leave. Keep upper-level management up to date with how the reward package is progressing against the company’s priorities and targets.
Financial Incentive Plan Design
Companies must first decide who will be eligible for incentive plans before implementing them. General compensation rules are as follows:
Occupational division (such as production or sales)
Duration of service and starting pay
Occupational division (such as executive or administrative)
No conflicts of interest
Individual Incentives vs. Group Incentives
Performance measures
Compensations and bonuses for salespeople
What will be included in the compensation package? (for example, bonuses, stock, or money)
When will the money be paid out? (every quarter or at the end of the year)
Incentive Programs for Financial Services
Plans for Long-Term Incentive:
A long-term incentive plan (LTIP) is a company-wide incentive plan that rewards employees for meeting specific goals that increase shareholder value. In a typical LTIP, the employee, who is usually a senior executive, must follow a set of regulatory requirements or conditions in order to be eligible for the bonus at the conclusion of the success cycle. A bonus is paid in addition to the executive’s base salary and is always in the form of cash. Discretionary compensation schemes for banking organizations are implemented by both private and publicly listed corporations based on a series of performance metrics.
Plans for Short-Term Incentive:
Employees are rewarded by fulfilling the company’s short-term strategic strategy based on the board appointment committee’s achievement of milestones for short-term incentives, also known as annual compensation.
Incentive Plans: What Are They and How Do They Work?
Be mindful that monetary incentives do not necessarily lead to the highest job results. Make employee benefits more personalized and valuable. When it comes to salary planning, pay close attention to the finer points and the true desires and wishes of the workers. Employee productivity and longevity improve as a result of this.
Define the mechanics and administration of the plan.
The bonus payment 0date and the success period should be tightly related. To strengthen the action, we suggest paying out as soon as possible. Compensation arrangements in the financial services industry, especially on Wall Street, are much more lucrative than in other industries. Since annual awards related to corporate earnings make up a large part of overall pay, there will be a lot of variation from year to year.
Expenses
Standard wage known as salary is considered base pay for bonus-eligible positions. At higher levels of administration, typically beginning with the vice president and other executive officers, salary is usually paid monthly rather than biweekly. Salary increases in the form of raises each year are common in executive compensation plans and are contingent upon the financial performance of the company.
Added Value
Annual incentive policies differ from one company to the next, but there are certain commonalities among them all. Bonuses are a larger percentage of net wages for more jobs on Wall Street and other financial services firms than they are for banks, holding companies, or insurance agencies, who are on the other end of the continuum. These incentive compensation practices mean that more of your salary would come in the form of bonuses when you advance up the management ladder of every sector. Your division’s or department’s incentive pool would be determined by a mix of the division’s and company’s income. Executives rarely use a formula to determine bonus pools; instead, they use a great deal of choice in terms of performance management.
Commissions
Commissions, unlike some other incentives, are very unpredictable. Employees who earn commissions (for example, financial advisors) are typically in sales roles. The compensation calculations are determined by the revenue earned by their clients as well as other main metrics such as the valuation of their clients’ accounts For commissioned work, payment is usually made monthly. To help balance risk, commissions help cut down on excessive compensation when a salary + commission structure is used.
What is a Clawback Provision, and how does it work?
In general, most corporate governance officers require that companies “clawback” incentive compensation awards paid to executives if the performance upon which those awards were based is later found to be erroneous. The came after the passage of the Dodd-Frank provisions. Most companies’ human resources departments and good corporate governance practices have implemented clawback policies in the last decade.
Bonuses are often controlled through clawback provisions in financial employment arrangements. Many incentives in complex financial instruments are paid out years after the sales are produced. If an employee’s success metrics drop, if they leave within a specified deadline, or if a customer churns within a certain timeframe or fails to fulfill an invoice, the clawback provision allows them to refund a portion of their pay or stock options. These can cause significant risk in interagency issues and material financial loss if an employee ends their contract early.
Sound Incentive Compensation Policies
Financial reporting companies discovered that analogous to insurance claims for “Acts of God,” they needed to shield their non-performing job payout plan after the financial crisis. The bulk of these incentive compensation arrangements clawback clauses are related to mortgages or mortgage-backed securities. The clawback clause has become more valuable in risk management as derivatives markets have grown. If the value of an investment drops, an employee is embroiled in a controversy or is fired for wrongdoing or unnecessary risk-taking, the company may recover a part of the compensation, plus interest for effective risk management.
Incentive compensation programs and clawbacks
To be subjected to a clawback, you don’t have to be guilty of misbehaving. Clawbacks are often used to facilitate employee retention, encourage better financial practices, and combat coercion with internal audits, theft, and accounting errors in bonus repayment. According to securities and exchange commission (SEC) regulations, clawbacks do not extend to compensation or incentives such as 401(k) contributions.
Reward Programs for Financial Services
Avoid the risks of making your source of record a spreadsheet that can be emailed throughout the organization, manipulated, and cause potential calculation errors. Nowhere is auditing and accountability more important than in the financial services space. With Compose you get transparency and real-time access to all accurate information and changes. A dynamic and accurate audit trail provides an assurance layer of protection for the firm and individuals. Decusoft is Compensation Management Software built for Financial Services.