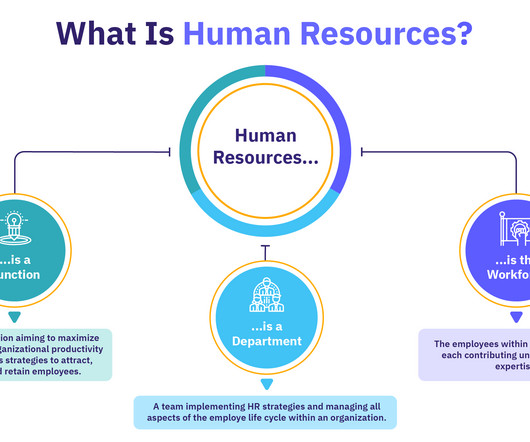
What Is Human Resources?
Analytics in HR
JULY 31, 2023
Managing Human Resources involves overseeing all aspects of HR, such as hiring, training, compensating, engaging, promoting, and retaining employees. HR: Facilitates strategic workforce planning to align talent with business objectives. Executes effective talent acquisition processes to hire the best talent for the right position.











Let's personalize your content