
In part five of John Sumser’s eigh-part series on security, John provides a quick and easy framework for thinking about the components of the Security Ecosystem.
Security Series 5 – The Ecosystem of Security Issues
Security involves a complex set of related factors ranging from attention to detail in maintenance, proper levels of concern for sensitive information, privacy, password management, hacking, competitive intelligence, identity management, infrastructure, financial issues, and more. Here is a quick and easy framework for thinking about the components of the Security Ecosystem:
- Business Continuity
The goal of an organization’s security program(s) is to ensure that the business can continuously to operate at an optimal level without unplanned interruptions, intentional or not. - Risk Management
Specific security concerns, practices and policies are a subset of the organization’s approach to understanding, anticipating and preparing for the various threats to continuous function. Beyond information and cyber security are market viability, competitive intelligence, supply chain management, and partner ecosystem design. All aspects of Risk Management happen within the context of the company and its culture. - Information Security (InfoSec)
At its most basic, InfoSec is procedures or measures used to protect electronic data from unauthorized access or use. One of the most basic tenets in InfoSec is the fact that there is ‘no such thing as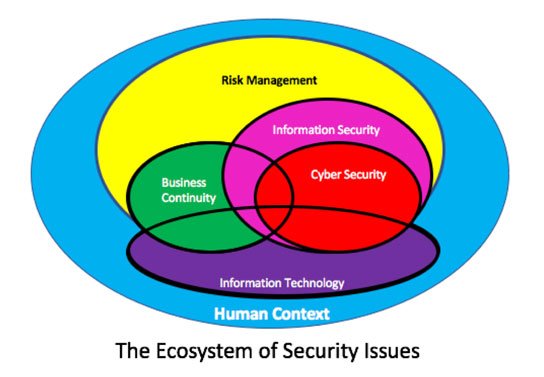 absolute security.’ The major subsets of this category are Personal Information (PI), Sensitive Personal Information (SI), Intellectual Property (IP), and Trade Secrets (TS). In the diagram, the area for InfoSec is larger than cyber security because there are so many different ways that information can be exposed.
absolute security.’ The major subsets of this category are Personal Information (PI), Sensitive Personal Information (SI), Intellectual Property (IP), and Trade Secrets (TS). In the diagram, the area for InfoSec is larger than cyber security because there are so many different ways that information can be exposed. - Cyber Security
The systems (hardware, software, infrastructure) that contain the company’s treasure trove of data and information are protected through password administration, technical systems upkeep, intentional design, and security access permissions. - Information Technology
In order to make the business work well, various elements of the operation are automated and or managed in the IT infrastructure. Security is a subset of operational IT and Risk Management. - Human Context/Culture
The primary users and administrators of strategic information are rarely the members of the IT staff. It’s much more likely that the security issues will come from users who are not well versed in underlying infrastructure questions. For this group, which includes working level employees, there is nothing more important than a well-kindled desire to help the company grow and prosper.
==========
The Security Series: HR as Security Leader
1: Overview – Why Focus Your HR Department on Security? Link »
2: Introduction Link »
3: Context – Shifting Technology Link »
4: Context – Increasing Employee Power Link »
5: The Ecosystem of Security Issues Link »
6: The Future of Security Issues Link »
7: The HR Security Center of Excellence Link »
8: Getting Started Link »











