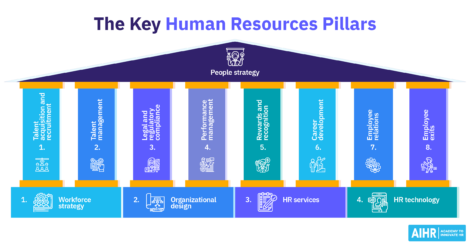
What is Human Resources?

Human Resources is both a function and a department within an organization.
As a function, HR covers the processes, practices, and strategies to attract, develop, and retain employees who contribute to the company’s overall success.
As a department, it is responsible for managing HR activities from recruitment and onboarding, compensation and benefits, learning and development, performance management, and employee relations to separation or retirement.
HR is vital in aligning the organization’s business objectives and employees’ needs and aspirations. Through workforce planning, talent management, succession planning, and applying other HR best practices, HR professionals ensure that the organization has the required talent to keep operating and meet its long-term goals.
They maximize employee capabilities that will help drive organizational success by identifying the skills gaps, creating L&D programs, and implementing performance management systems.
Human Resources also refers to the workforce or people employed in an organization. In this view, HR recognizes that employees are a company’s most critical asset. Hence, they execute an HR strategy to create a supportive and engaging work environment that values employees’ contributions and wellbeing.

What is HR Management?
Human Resources Management (HRM) is a systematic approach to managing the company’s workforce to help meet organizational goals. Managing Human Resources involves overseeing all aspects of HR, such as hiring, training, compensating, engaging, promoting, and retaining employees.
For example, your HR would look into hiring people who are a good culture fit for the organization so they stay longer and be more productive. Or implement various employee engagement strategies to motivate employees so they perform better.
Overall, HR Management’s role extends beyond administrative functions. It is instrumental in shaping the company’s strategic direction and fostering a thriving, inclusive, and high-performing work environment.
Strategic Human Resources
Strategic Human Resources, or Strategic Human Resources Management, refers to a more advanced approach to aligning HR strategies with the organization’s overall strategy and objectives.
In HR strategic planning, the HR department works closely with the management team and business leaders to study current and future staffing requirements, determine skill gaps, and enforce HR tactics that will attract, grow and retain the most talented individuals.
It includes reviewing organizational and HR metrics to measure HR initiatives’ effectiveness on business results. It could also involve staying updated with the latest technology developments and market trends to ensure the company stays relevant and competitive.

What does HR do? HR functions

HR performs numerous Human Resources functions in an organization. Let’s go over the 12 key HR functions:
- Human Resources planning – The systematic and data-driven practice of optimizing the company’s workforce. The goal is to ensure the company is adequately staffed with the right people to avoid surpluses or shortages.
- Recruitment and selection – Attracting and hiring applicants that are best for the job, which involves many steps: writing job descriptions, screening resumes and shortlisting candidates, conducting job interviews, creating job offers, and onboarding the selected candidate.
- Performance management – The ongoing process of managing the employees’ performance and development in alignment with the company goals. It includes communicating and clarifying job responsibilities, expectations, and priorities.
- Learning and development – Providing opportunities to develop the employees’ skills and knowledge to improve performance, which ultimately leads to both the individual and company’s success.
- Career planning – Also called career pathing, HR provides guidance and ongoing support to help employees progress in their career, whether vertically (promotion) or horizontally (lateral transfers). Internal mobility helps organizations improve employee engagement and retention while reducing hiring costs.
- Function evaluation – HR staff compares the different teams of the whole HR operation, which includes the quality and the availability of employees, job location, working hours, the economic situation, other job responsibilities, and how much value a job contributes to the organization.
- Rewards – An integral part of Human Resources duties, rewards are an essential motivator for employees. They can sometimes be the primary reason employees choose one company over another. Rewards include salary, perks, and benefits like health insurance, remote work, and performance-based bonuses.
- Industrial relations – Maintaining good relationships with labor unions and other collectives and their members help in detecting and resolving potential conflicts before it escalates, especially during challenging situations like layoffs.
- Employee participation and communication – HR delivers relevant and timely information to employees. Maintaining open and honest communication fosters an environment of trust and support, which is vital to employee retention.
- Health and safety – A critical part of HR responsibilities is ensuring employees work in an environment compliant with health and safety guidelines to avoid injuries, illnesses, and deaths.
- Wellbeing – Another key function of HR is looking after their staff’s mental, physical, and financial wellbeing because people work best when they feel best. This may include implementing wellness initiatives to address mental health, for example.
- Administrative responsibilities – Performing administrative work like maintaining the HRIS where employees’ information is stored.

Why is Human Resources important?

The Human Resources function plays a pivotal role in the organization for various reasons. Let’s take a look at some of them. HR:
- Facilitates strategic workforce planning to align talent with business objectives.
- Executes effective talent acquisition processes to hire the best talent for the right position.
- Helps foster a positive organizational culture by implementing practices that improve employee engagement and retention.
- Administers employee benefits and compensation that enhance employees’ satisfaction and financial security.
- Can roll out initiatives to boost employee productivity by launching learning and development programs, performance management tactics, and incentive programs to motivate employees to do better.
- Can help the organization save money by optimizing recruitment processes or decreasing employee absenteeism or turnover.
- Can boost employee morale by effectively managing conflicts, concerns, and grievances.
- HR ensures compliance with employment laws and regulations to protect employees’ rights.
- HR supports organizational development by building organizational capabilities and improving processes and strategies.
But how exactly does HR help the organization achieve its goals and objectives?
We can illustrate this with the HR value chain. Simply said, the HR value chain demonstrates the connection between HR Management activities and processes, HR Management outcomes, and the organization’s strategic goals.
Carrying out HRM activities results in positive HRM outcomes, which leads to achieving corporate objectives. Let’s break this down.
- HRM activities and processes – Daily tasks performed by HR, such as recruitment, training, and talent management. How well these activities are done indicates the efficiency of HR, and the goal is to achieve certain outcomes.
- HRM outcomes – HRM activities and processes aim to improve employee engagement, retention, competency levels, and performance, as well as decrease absenteeism. These are the HRM outcomes.
- Organizational objectives – Success in achieving HRM outcomes positively impacts the company’s ability to attain its strategic goals the company. These goals add value to the business and put the organization more viable in the long run.
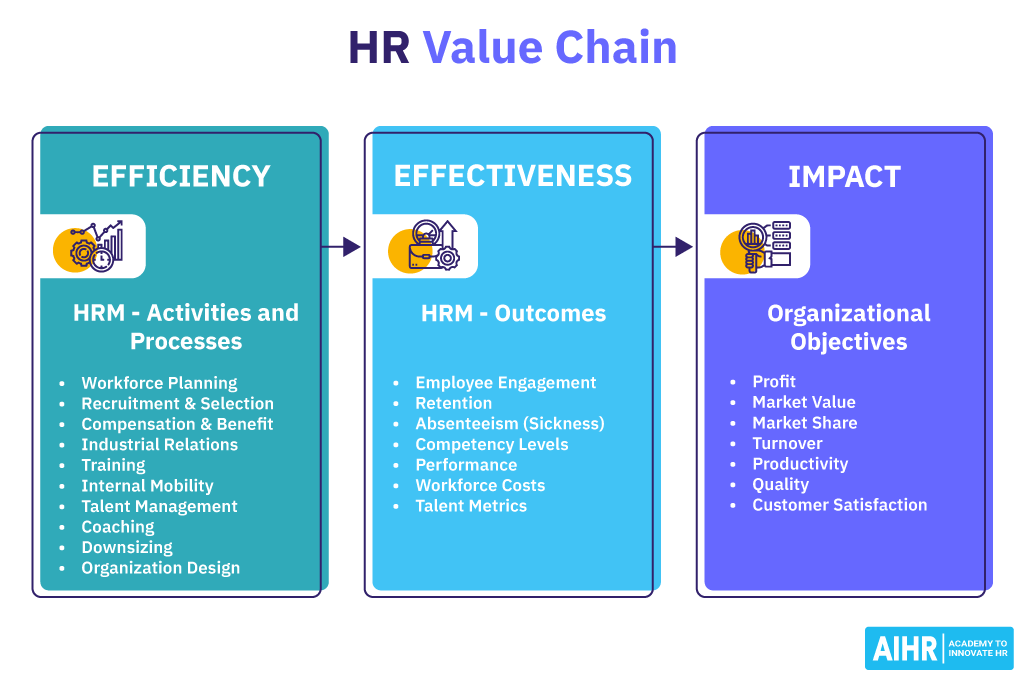
By understanding how HR creates value for an organization, HR professionals can ensure that their practices align with organizational objectives, ultimately contributing to the overall success and competitiveness of the business in the long run.
Human Resources examples

What does the Human Resources function look like in practice? Here are two examples of what HR does in two well-known organizations:
Google is renowned for its innovative HR practices that have earned it a reputation as one of the best places to work globally:
- Flexible work arrangements – The company offers flexible work hours and remote working. They even permit their workforce to work on their projects for 20% of their time. These work arrangements promote work-life balance and increase creativity and innovation. Moreover, Google evaluates their employees’ productivity not by the number of hours worked but by results and contributions.
- Data-driven HR – Google uses people analytics extensively in its HR practices to make informed decisions. They leverage data to gain insights into their workforce, identify trends, and tailor HR strategies accordingly. Google’s People Innovation Lab (PiLab) conducts research around “making work better in and outside of Google” and shares their findings with the world. For example, the company’s Project Oxygen analyzed massive amounts of internal data and determined what makes great managers, incorporating the findings into the company’s manager development programs and sharing their recommendations publicly.
FedEx
FedEx designs their HR strategies, policies, and initiatives to align with the principles of their ‘People-Service-Profit’ philosophy, ensuring that employees’ well-being and development are prioritized to drive excellent customer service, contributing to the company’s profitability. The company defines the three components as follows:
- People: Putting people first means valuing employees as the company’s most valuable asset
- Service: The focus on delivering exceptional customer service and ensuring that customers’ needs are met with efficiency and excellence
- Profit: By caring for its people and delivering outstanding service, FedEx believes it will generate long-term profitability and sustain business success
Prioritizing employee development and satisfaction has enabled FedEx to maintain an engaged and motivated workforce, leading to higher productivity and lower turnover rates.
The focus on customer service resulted in higher customer satisfaction levels, strengthening FedEx’s reputation in the logistics industry. By emphasizing long-term profitability through a well-supported workforce and exceptional customer service, FedEx has experienced steady growth and financial success.
Additionally, the PSP philosophy has helped shape a positive company culture where employees feel valued and committed to giving their best for the customers and the company.

The HR department

What does the HR department do?
HR department carries out HR functions like recruitment, rewards, and HR planning within an organization. The structure and responsibilities depend on the company’s size, structure, and industry.
Small businesses
(10-99 employees)In small companies, an HR professional handles all HR functions, such as recruitment, performance management, compensation, and benefits, employee relations, and HR administration. Their responsibilities are more tactical and administrative like:
– Writing job offers and employment contracts
– Handling logistics when onboarding new employees
– Managing payroll
– Document company policies, guidelines, and processes
They typically report directly to the CEO but may also report to the COO or Head of Operations.Mid-sized businesses
(100-999 employees)For mid-sized companies, HR duties may expand to include training and development, employee engagement and culture, and HR strategy and planning. For example, they:
– Develop employee wellness or recognition initiatives,
– Implement different learning and development programs,
– Conduct workforce planning, and
– Plan and execute organizational development strategies to support the company’s growth and future needs.
The Human Resources department may be headed by a VP of HR, who will manage an HR Director and a Director of Talent Acquisition. The directors may lead teams of managers and specialists.Large businesses
(1,000+ employees)In large organizations, there would be more staff with more specialized functions in managing the complexities of a large and diverse workforce. HR scope broadens further to include strategic workforce planning, employee retention, diversity and inclusion, HR systems and technology, and HR strategy and leadership.
For instance, the HR team would perform the following duties:
– Skills gap analysis
– Employer branding
– Recruitment marketing
– Succession planning
– Compensation benchmarking
– Managing HR software
– Change management
– Executing DEI initiatives
Successful execution of these functions would require a more complex HR organization. Roles could include Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO), Chief Diversity Officer, HR Business Partner, HR Analyst, Training/L&D Director, and Employee Relations Officer in addition to the HR Managers, HR Specialists, HR Generalists, and other roles like recruiters, sourcers, and payroll specialists.
CHRO is usually part of the executive team in large organizations, reporting directly to the CEO.
Here’s a sample HR organization chart for a mid-sized business:

Who is above HR in a company?
The HR department usually reports directly to the CEO or other members of the C-suite, like the COO.
Sometimes, there might be multiple management levels, such as department heads or Vice Presidents, that lie between the HR department and the top executives. This varies based on the organizational structure.
Regardless of the structure, the ultimate authority remains with the executive leadership team at the top of the company hierarchy.
HR roles
Depending on the structure and responsibilities of an HR department, the team will define what roles they need to effectively manage all aspects of Human Resources. By determining the right roles and responsibilities, the HR department ensures it can effectively support both the employees and the organization’s broader objectives.
Let’s take a look at some common HR roles.
HR Generalist
HR Generalist performs a broad range of HR responsibilities rather than a specialized HR function. They’re involved in activities like recruitment, compensation and benefits, performance management, training and development, and employee engagement.
Typical responsibilities are:
- Assisting in recruitment and onboarding, like screening candidates, performing job interviews, conducting reference checks, sending employment offers, and handling company orientation and logistics for new hires
- Updating and maintaining employee files, benefits, and attendance records
- Assisting in payroll processing, which includes sick/vacation pay, bonuses, and benefits changes
- Generating and submitting HR reports
- Producing internal documents like offer letters, appointment letters, salary slips, and warning letters
- Helping in the development and implementation of HR policies
HR Generalist salary
HR Generalist salary varies based on industry and location. According to Glassdoor, the average annual wage for an HR Generalist across all industries is around $64,800. On average, HR Generalist working in the telecommunications sector earns $62,086 annually, while those employed in financial services receive $71,818 annually.
Meanwhile, PayScale reports the average annual salary of HR Generalists to be $73,207 in New York and $61,899 in Dallas, Texas.
HR Specialist
Human Resources Specialists usually concentrate on a specific HR function. Their responsibilities also include assisting with other HR tasks, but their main focus is their area of specialization.
For example, an HR Specialist could be responsible for recruitment and onboarding in that case, their duties would include:
- Posting job openings
- Resume and phone screening
- Conducting background and reference checks
- Preparing onboarding kits for new hires
- Organizing job orientation for new employees
HR Specialist salary
HR Specialists can earn anywhere between $21,000 and $87,000. In Chicago, HR Specialists are paid $64,805 annually, while their New York colleagues take home $70,260 annually. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that the employment of Human Resources Specialists will increase by 8 percent by 2031.
HR Manager
The Human Resources Manager oversees (part of) the HR department. They have other HR employees reporting directly to them.
Common HR Manager responsibilities are:
- Managing HR activities like recruitment, learning and development, compensation and benefits, employee relations, and other HR functions
- Developing and implementing HR programs and policies that support organizational goals
- Working with other department heads to address workforce needs, from staffing shortages to skills development
- Managing the HR budget – Reviewing past HR budgets and analyzing and forecasting the company’s workforce requirements to manage the cost of human capital and ensure the department’s operational efficiency
- Report on HR metrics to senior management – These metrics include workforce headcount, turnover, cost per hire, training cost per employee, eNPS, human capital ROI
HR Manager salary
According to Glassdoor, Human Resources managers in Chicago are paid $83,722 annually, while New York-based HR managers based receive $111,857 per year.
The average salary also varies by years of experience. HR managers with 1-3 years of experience earn $85,788 yearly. Those with 10-14 years get $112,034 annually.
In a report by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the employment of Human Resources Managers is projected to grow 7 percent by 2031.
HR Business Partner
A Human Resources Business Partner provides guidance and assistance to line managers in implementing HR best practices that support the company’s business strategy.
Some of the typical responsibilities of an HR Business Partner include:
- Providing strategic advice in workforce planning, upskilling, and succession planning
- Advising business leaders in HR areas of expertise like employee relations, performance management, learning and development, and compensation.
- Assisting in HR policies development and implementation
- Helping organizations tackle current business challenges using HR strategies
- Help line managers address issues related to organizational design and people management
- Analyze HR metrics to identify trends and areas for improvement and create action plans to resolve them
- Stay updated on employment laws and regulations to help leaders ensure compliance
Salary
Payscale estimates that the average HR Business Partner salary in the United States is $78,931 annually. Pay depends on years of work experience, education, certifications, industry, and additional skills.
The average income also depends on location. Payscale states that the yearly salary of an HR Business Partner in Chicago is $83,135, while their New York counterparts receive $95,536 per year.
There are also many other roles in Human Resources, which are often more specialized. They can focus on, for example, people analytics, DEIB, or talent acquisition.

Human Resources career
A career in Human Resources can be gratifying as it opportunity to make a strategic impact on an organization and its people. HR professionals also have the chance to continuously develop their skills and play a key role in shaping an organization’s culture and growth.
There are over 805,000 HR professionals in the US, and the demand for HR services and software continues to grow. By 2030, the market will grow at a rate of 12.7% annually.
How to get into HR
Whether you are a new graduate eager to pursue an HR job or an experienced professional interested in switching careers, here are some tips to kick-start your HR career:
- Get certified – An HR certification program is a great way to learn about the fundamentals of Human Resources and get formal credentials in the field. Look for online training programs suitable for beginners, which you can start anytime at your own pace.
- Learn basic HR skills – Focus on developing relevant HR skills like communication, administrative expertise, coaching, and recruitment.
- Use free HR resources – Plenty of resources are available to stay abreast of the latest HR trends and developments. Subscribe to newsletters, listen to HR podcasts, and read HR blogs to learn more about what’s happening in the world of Human Resources.
- Join HR network and industry groups – Gain insights from seasoned HR professionals of all levels and industries. You may even land your next job from friends or colleagues within these associations.
- Volunteer or apply for an internship – Your company may have an HR or recruitment project drive you can participate in to get hands-on experience of what it’s like to work in HR.
HR career path
HR offers professionals various possibilities to design their career paths, change between different specializations, and continuously develop their skills. With HR’s growing strategic importance, individuals can find meaningful career options that align with their interests and abilities.
Mapping one’s HR career path involves identifying the desired skills and professional experience and aligning them with different HR positions and profiles.
At AIHR, we’ve identified four career tracks. While each HR career path requires specific core skills and behavior, you can also plan what you need to learn and gain experience in to move onto a different path. These are the four HR career paths:
- Advisory – Acting as a trusted HR expert by delivering solid and sound advice relevant to the organization’s current business environment and needs. This track includes positions like HRBPs, Senior HRBPs, and HR Consultants.
- Solution Provider – Responsible for designing practical and sound HR practices that address the company’s business needs. Roles in this career path include Learning and Development Consultants, Industrial Relations Specialists, or OD Specialists.
- Service Provider – Responsible for delivering fast and quality service. Roles are usually more junior or middle-management levels: HR Administrator, Payroll Manager, Benefits Manager, or HR Scrum Manager.
- Strategic – Key contributor to the business strategy and partner by planning the company’s future direction. These are experienced HR leaders who work across a variety of HR functions. Positions include HR Director, Shared Services Manager, or Chief Human Resources Officer.
FAQ

Human Resources is the department in a company that handles everything related to its employees. It has a wide array of responsibilities, from leading the hiring process and onboarding new staff to managing employee benefits, training and development programs, and resolving workplace issues.
The goal is to enable the workers to be productive, which, in turn, helps the organization achieve success.
Human Resources plays a vital role by ensuring the company’s most important asset – its workforce – is well cared for. HR is tasked with attracting, managing, developing, and retaining employees who drive the company’s success.
HR supports employees throughout their entire life cycle at the organization: from hiring through onboarding all the way until after an employee leaves the organization.
HR offers learning and development programs to support employees’ career development. The HR department also manages the compensation and benefits to ensure employees receive fair and competitive remuneration and benefits that support their wellbeing.
Yes, Human Resources is responsible for the recruitment and hiring of employees. Recruiters and Talent Acquisition Specialists usually screen resumes, conduct job interviews, write job offers, and onboard the selected candidates. HR works with the hiring manager for the candidate recruitment and selection process.
Yes, the HR department is often responsible for payroll administration. The payroll process involves collecting employee information like attendance and time records and calculating and processing employee salaries and benefits in compliance with labor laws and company policies.
An HR Generalist, Payroll Specialist, or Payroll Manager manages payroll.
Human Resources can be a rewarding and fulfilling career for individuals who want to create a positive impact on the business and its employees.
In modern organizations, HR is increasingly seen as a strategic partner that aligns people’s practices with business goals, which makes HR professionals valued contributors to the overall success of the company. What’s more, with the evolving employee-employer relationship and the emergence of innovative new tools and Artificial Intelligence, HR provides great opportunities for professional development and continuous learning.
In terms of demand, every organization requires Human Resources professionals to manage their workforce effectively, so HR talent is always needed across various industries and sectors.