How incentive theory drives motivation and behavior in the workplace
Achievers
NOVEMBER 29, 2024
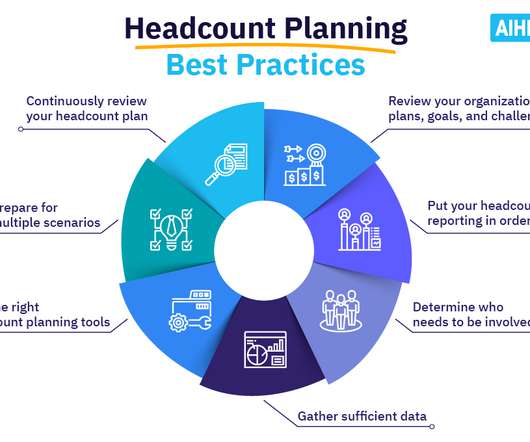
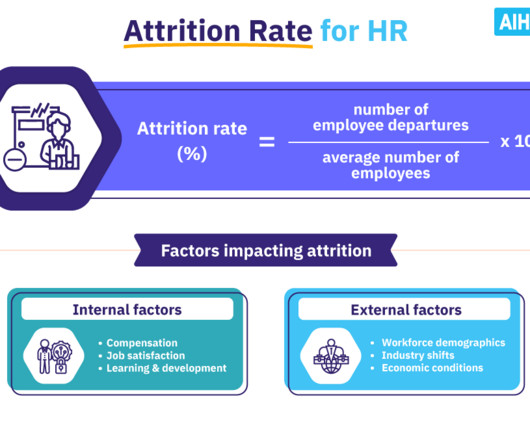
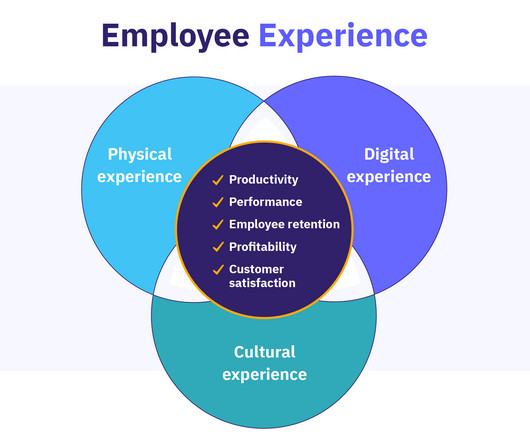
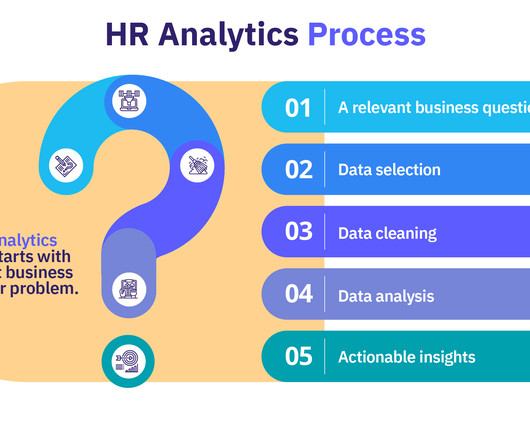
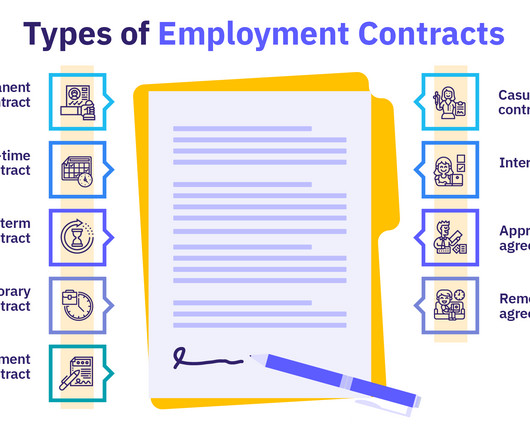
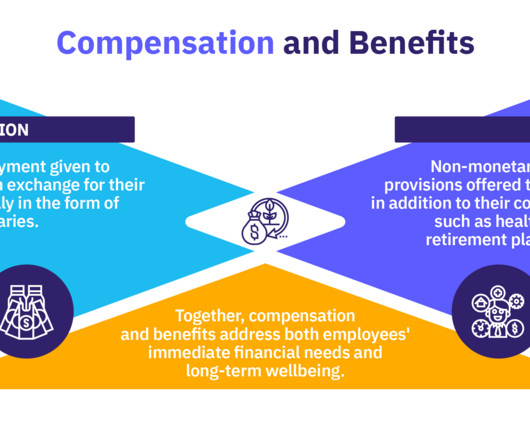
Incentive theory offers valuable insights into what drives employee motivation in the workplace. Whether it’s a financial perk, professional growth opportunity , or simple recognition, incentives help create a culture where employees feel valued and motivated to contribute their best. What is incentive theory?












































Let's personalize your content